Perpetual futures trading has become one of the most dominant segments of the digital asset market, accounting for a significant share of global crypto derivatives volume. As this market matures, a clear structural shift is underway: perpetual futures trading is increasingly moving from centralized venues to decentralized perpetual exchanges. This transition is not merely philosophical; it is rooted in the architectural robustness, transparency, and resilience offered by decentralized systems.
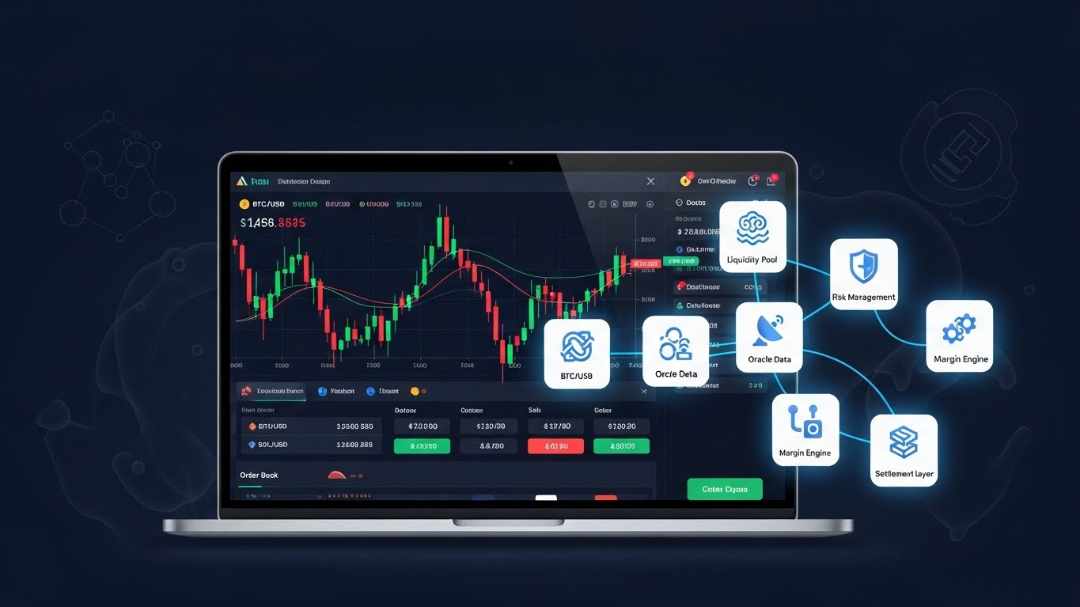
At the heart of this evolution lies the Perpetual Futures Trading DEX Platform, a complex, multi-layered infrastructure composed of tightly integrated modules. Each module performs a critical function, and together they determine the platform’s performance, security, capital efficiency, and long-term viability. Understanding these core modules is essential for anyone involved in Perpetual Exchange Development, whether as a builder, investor, or advanced market participant.
This article explores the foundational modules that power modern decentralized perpetual exchanges, explaining how they interact, why they matter, and how thoughtful design choices differentiate production-grade platforms from experimental implementations.
The Architectural Philosophy Behind Perpetual DEX Platforms
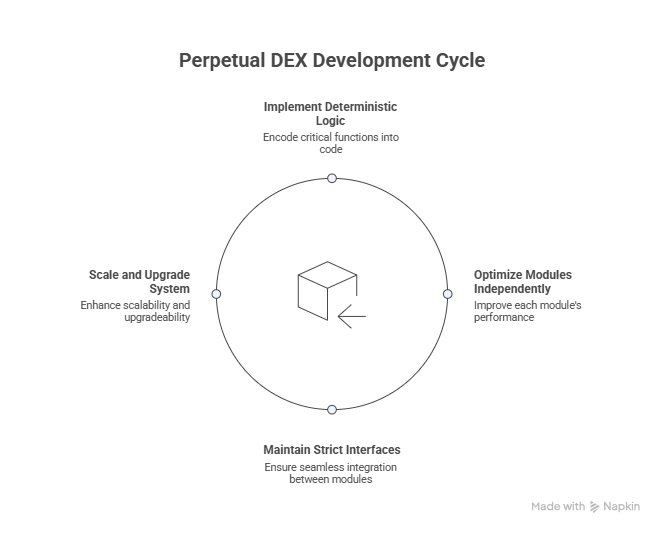
Before examining individual modules, it is important to understand the architectural philosophy guiding Perpetual DEX Development. Unlike centralized exchanges, which rely on proprietary infrastructure and discretionary controls, decentralized perpetual exchanges operate as protocol-driven systems. Every critical function—risk management, settlement, pricing, and liquidation—is encoded into deterministic logic.
This modular approach is intentional. In Decentralized perpetual exchange development, modularity allows for scalability, composability, and upgradeability without destabilizing the entire system. Each module can be optimized independently while maintaining strict interfaces with other components. This design principle has become a defining feature of mature Perp DEX Platform Development.
Margin and Collateral Management Module
The margin and collateral management module is the foundation of any perpetual futures trading system. It governs how collateral is deposited, valued, locked, and released across trader positions.
In a Perpetual Futures Trading DEX Platform, this module continuously evaluates user collateral against open positions and market prices. Unlike centralized platforms, where margin logic often operates off-chain and lacks transparency, decentralized systems enforce margin requirements directly through smart contracts.
This module determines initial margin requirements, maintenance margin thresholds, and available leverage. It must account for volatile price movements in real time, ensuring that positions remain sufficiently collateralized. Poorly designed margin systems can lead to cascading liquidations or protocol insolvency, making this module a focal point in Perpetual Futures Trading DEX Platform development.
Modern platforms often support cross-margin functionality, allowing traders to share collateral across multiple positions. While this improves capital efficiency, it also increases systemic complexity, requiring sophisticated risk modeling within the margin engine.
Position and Account State Management Module
Closely tied to collateral logic is the position and account state management module. This component tracks every trader’s open positions, entry prices, position sizes, unrealized profit and loss, and funding payments.
In decentralized environments, maintaining accurate and gas-efficient position accounting is technically challenging. The module must update states continuously while minimizing on-chain computation costs. Advanced Decentralized perpetual exchange development solutions employ optimized data structures and batched state updates to balance accuracy with scalability.
This module is also responsible for enforcing deterministic outcomes. Given the same inputs—prices, funding rates, and collateral—the system must always produce the same results. This predictability is one of the key trust advantages of decentralized perpetual exchanges over centralized platforms.
Trade Execution and Matching Module
Trade execution is where user intent is transformed into on-chain state changes. Early decentralized perpetual exchanges struggled in this area due to latency and high transaction costs. Today, trade execution has become one of the most sophisticated modules in Perpetual DEX Development.
Most modern platforms use hybrid execution models. Trade orders are often matched or validated off-chain for speed, while final settlement occurs on-chain for trustlessness. The execution module verifies that each trade complies with margin requirements, leverage limits, and risk parameters before committing it to the blockchain.
This module plays a crucial role in user experience. Execution delays, failed transactions, or inconsistent fills can undermine trader confidence. As a result, trade execution is a core focus area for any Perpetual DEX Development Company aiming to build institutional-grade infrastructure.
Pricing and Oracle Integration Module
Accurate pricing is the lifeblood of perpetual futures markets. Every margin check, liquidation trigger, and funding calculation depends on reliable price data. The pricing and oracle integration module is therefore one of the most security-sensitive components in a Perpetual Futures Trading DEX Platform.
Decentralized platforms typically rely on external oracle networks that aggregate prices from multiple spot and derivatives markets. The module applies filters, averaging mechanisms, and time-weighted calculations to mitigate manipulation and short-term volatility.
In advanced Decentralized perpetual exchange development, pricing logic may incorporate multiple reference prices, including mark price, index price, and last traded price, each serving a specific function within the system. This layered approach reduces the risk of oracle attacks and improves market stability during periods of extreme volatility.
Funding Rate Calculation Module
Funding rates are the mechanism that aligns perpetual contract prices with underlying spot markets. The funding rate calculation module continuously evaluates price deviations and determines periodic payments between long and short positions.
In decentralized systems, funding logic must operate autonomously and transparently. Smart contracts calculate funding rates based on predefined formulas and distribute payments directly between traders without intermediaries.
This module is not merely a mathematical function; it is a market-balancing tool. Poorly calibrated funding models can drive traders away or create persistent imbalances. As a result, funding rate design is a critical consideration in Perpetual Futures Trading DEX Platform development and often reflects deep market microstructure expertise.
Risk Management and Liquidation Module
Risk management is where decentralized perpetual exchanges most clearly diverge from centralized platforms. In a Decentralized perpetual exchange, risk controls are embedded directly into protocol logic rather than enforced by human operators.
The liquidation module monitors all open positions and triggers liquidations when maintenance margin thresholds are breached. Liquidations may be partial or full, depending on platform design. Some systems use competitive keeper networks to execute liquidations efficiently, while others rely on internal mechanisms or backstop liquidity pools.
This module must balance speed and market impact. Overly aggressive liquidations can destabilize markets, while delayed liquidations increase protocol risk. Achieving this balance is one of the most complex challenges in Perpetual DEX Development Services.
Liquidity and Market-Making Module
Liquidity provision is central to the usability of any perpetual trading platform. Unlike centralized exchanges that rely heavily on proprietary market makers, decentralized perpetual exchanges must design liquidity systems that function autonomously.
Many platforms use virtual automated market makers or hybrid liquidity vaults that dynamically adjust pricing curves based on market conditions. These systems allow liquidity providers to earn fees while supporting deep markets across multiple trading pairs.
In mature Perp DEX Platform Development, liquidity modules are tightly integrated with funding rate logic and risk controls, ensuring that liquidity remains balanced even during volatile periods. This integration has been key to overcoming early liquidity limitations in decentralized perpetual markets.
Settlement and Clearing Module
Settlement is the process by which trades are finalized and account states are updated. In decentralized systems, settlement is inseparable from execution, as both occur through smart contracts.
The settlement module ensures that collateral transfers, PnL realization, and funding payments are applied atomically. This atomicity eliminates counterparty risk, a major weakness of centralized derivatives platforms.
In Perpetual Exchange Development, settlement design must also consider scalability. Layer-2 networks and rollups are increasingly used to reduce costs and increase throughput without sacrificing security.
Governance and Upgrade Module
No perpetual exchange can remain static. Market conditions, regulatory landscapes, and user demands evolve over time. Governance modules enable decentralized platforms to adapt without central control.
Through governance mechanisms, token holders or designated stakeholders can propose and vote on parameter changes, feature upgrades, or risk adjustments. Well-designed governance frameworks strike a balance between decentralization and operational efficiency.
In Decentralized perpetual exchange development, governance is increasingly viewed as a core infrastructure module rather than an auxiliary feature.
Security, Monitoring, and Analytics Module
Given the financial stakes involved, continuous monitoring is essential. Security and analytics modules track protocol health, open interest, liquidation activity, and liquidity distribution in real time.
These insights help developers and governance participants identify emerging risks before they escalate. From a user perspective, transparency builds trust and encourages participation.
For any Perpetual DEX Development Company, robust monitoring infrastructure is a prerequisite for long-term credibility.
How These Modules Work Together
While each module serves a distinct purpose, the true strength of a Perpetual Futures Trading DEX Platform lies in how these components interact. Margin logic depends on oracle prices. Liquidations rely on margin calculations. Funding rates influence liquidity distribution. Governance shapes all of them over time.
This interconnectedness means that Perpetual Futures Trading DEX Platform development cannot be approached piecemeal. A weakness in one module can compromise the entire system, underscoring the importance of holistic design and rigorous testing.
Conclusion
The rise of decentralized perpetual exchanges reflects a broader transformation in financial infrastructure. By decomposing trading systems into transparent, modular components, Decentralized perpetual exchange development has redefined how derivatives markets can be built and governed.
The core modules of a perpetual futures trading DEX platform—margin management, execution, pricing, risk control, liquidity, and governance—are not merely technical building blocks. They represent a new paradigm of market design, one that prioritizes transparency, resilience, and user sovereignty.
As Perpetual DEX Development continues to mature, platforms that master these core modules will set the standard for the next generation of global derivatives trading.

















Write a comment ...